Intro ...
Cubic Hermite Interpolation
Intro ...
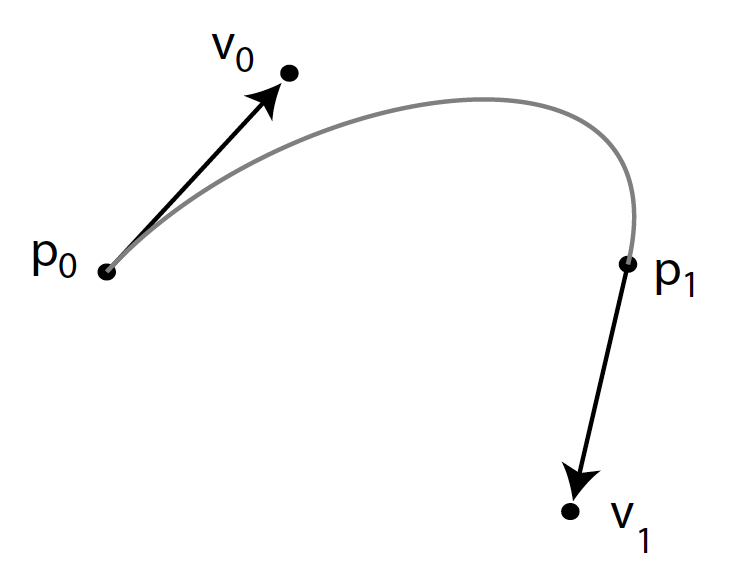
We look for a curve
$$
c(t) = a_0 + a_1 t + a_2 t^2 + a_3 t^3
$$
that satisfies
$$
\begin{cases}
c(0) = p_0, \quad c^{\prime}(0) = v_0 \\
c(1) = p_1, \quad c^{\prime}(1) = v_1
\end{cases},
$$
or we should solve the following system
$$
\begin{cases}
p_0 = a_0 \\
v_0 = a_1 \\
p_1 = a_0 + a_1 + a_2 + a_3 \\
v_1 = a_1 + 2a_2 + 3a_3
\end{cases}.
$$
which gives us the curve parameters we want in terms of the given data
$$\begin{cases}
a_0 = p_0 \\
a_1 = v_0 \\
a_2 = 3p_1 - 3p_0 - 2v_0 - v_1 \\
a_3 = -2p_1 + 2p_0 + v_0 + v_1
\end{cases}.
$$
If we rearrange the terms for \(c(t)\) we get
$$
c(t) = (1 - 3t^2 + 2t^3)p_0 + (t - 2t^2 + t^3)v_0 + (-t^2 + t^3)v_1 + (3t^2 - 2t^3)p_1
$$
or in basis function form
$$
c(t) = H_0^3(t)p_0 + H_1^3(t)v_0 + H_2^3(t)v_1 + H_3^3(t)p_1,
$$
where
$$
\begin{cases}
H_0^3(t) = 1 - 3t^2 + 2t^3 \\
H_1^3(t) = t - 2t^2 + t^3 \\
H_2^3(t) = -t^2 + t^3 \\
H_3^3(t) = 3t^2 - 2t^3
\end{cases}.
$$
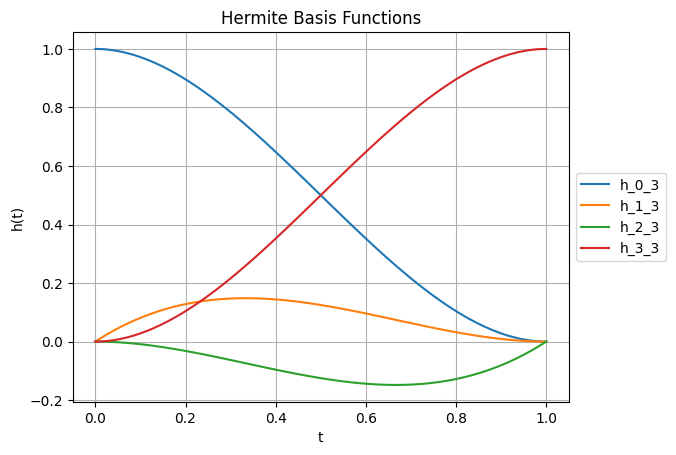
Plotting the Cubic Hermite basis functions
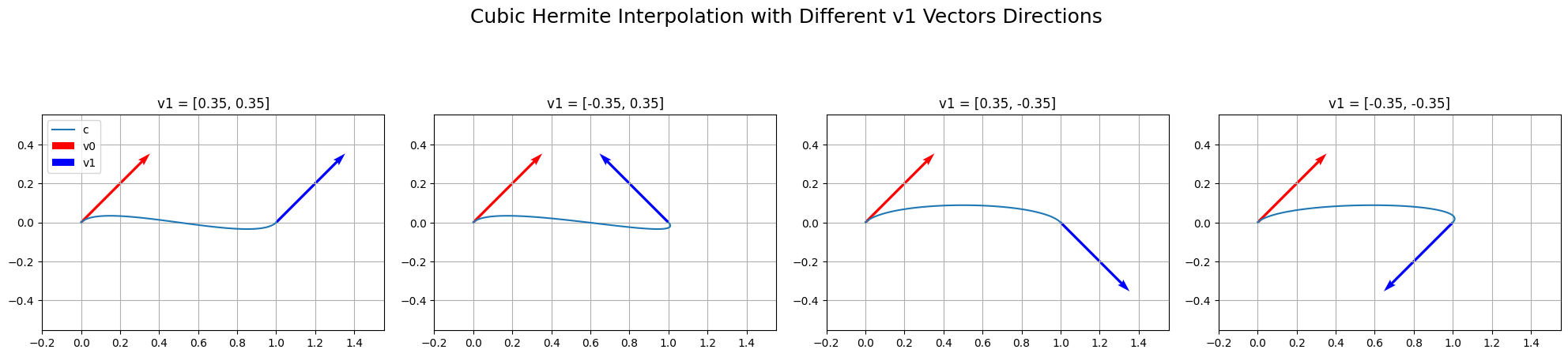
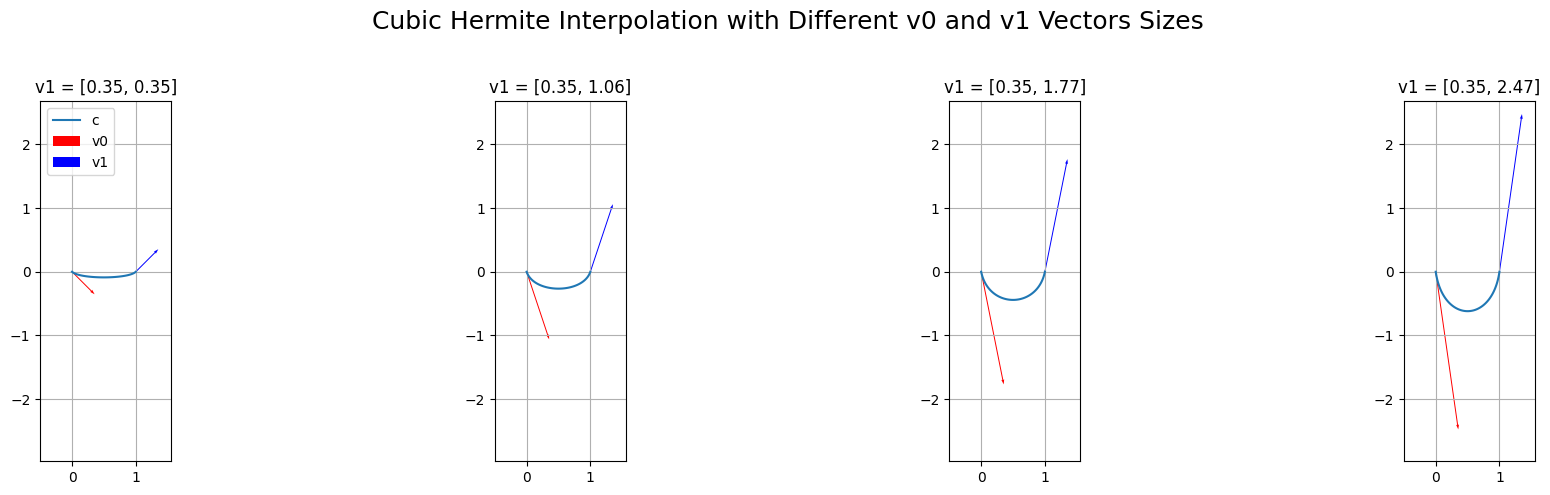
Examples
Some text
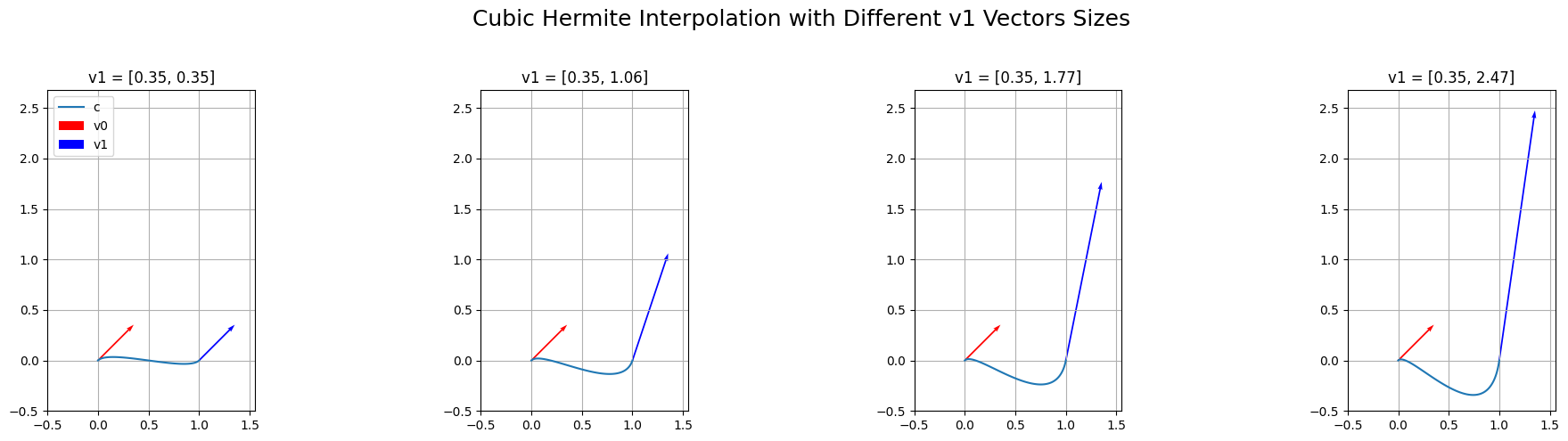
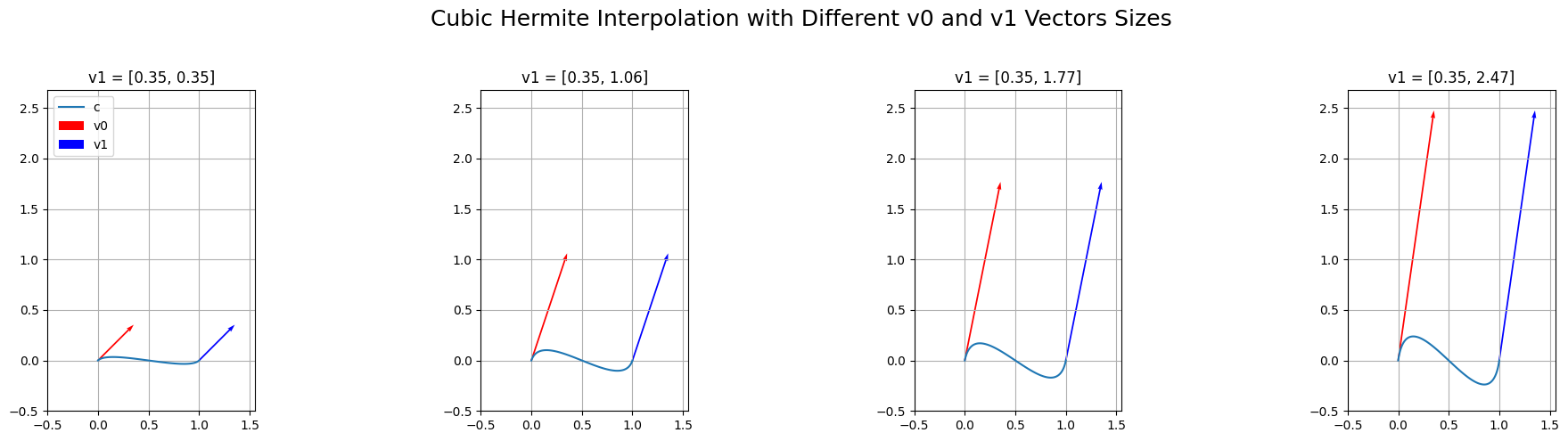
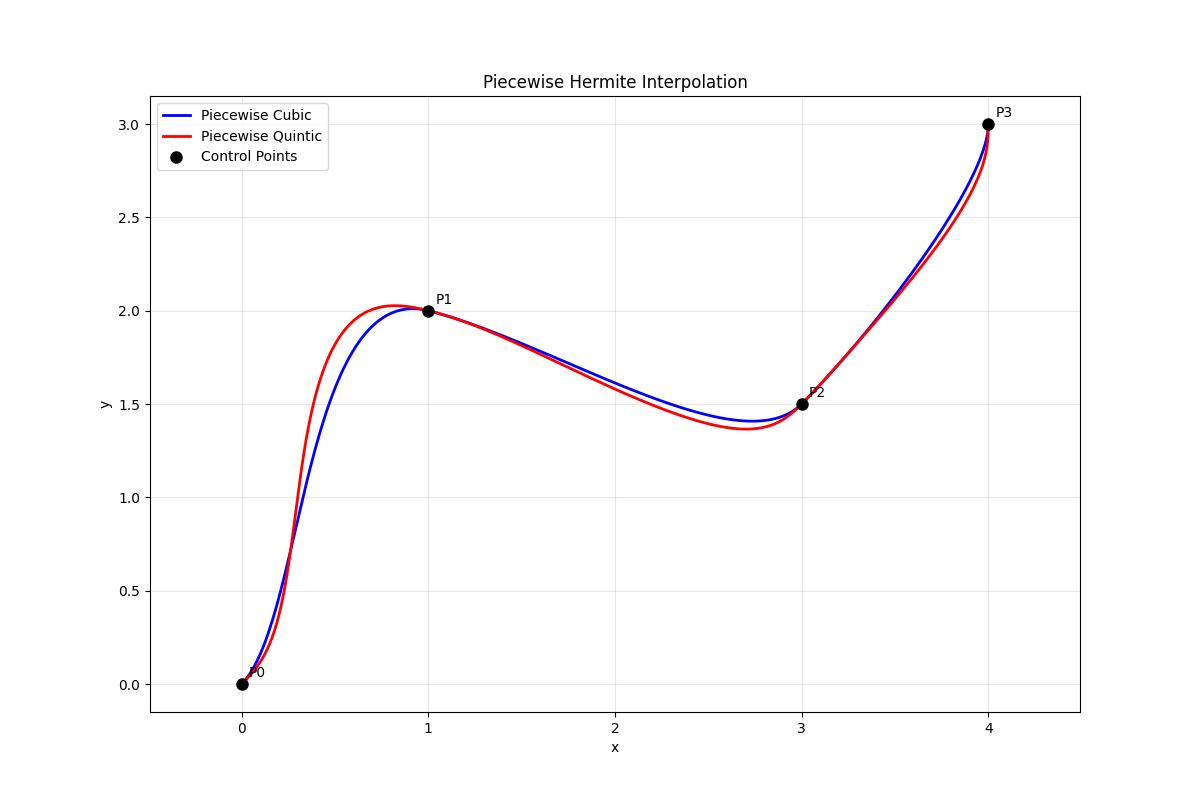
Quintic Hermite Interpolation
Piecewise Curves: Building Complex Paths
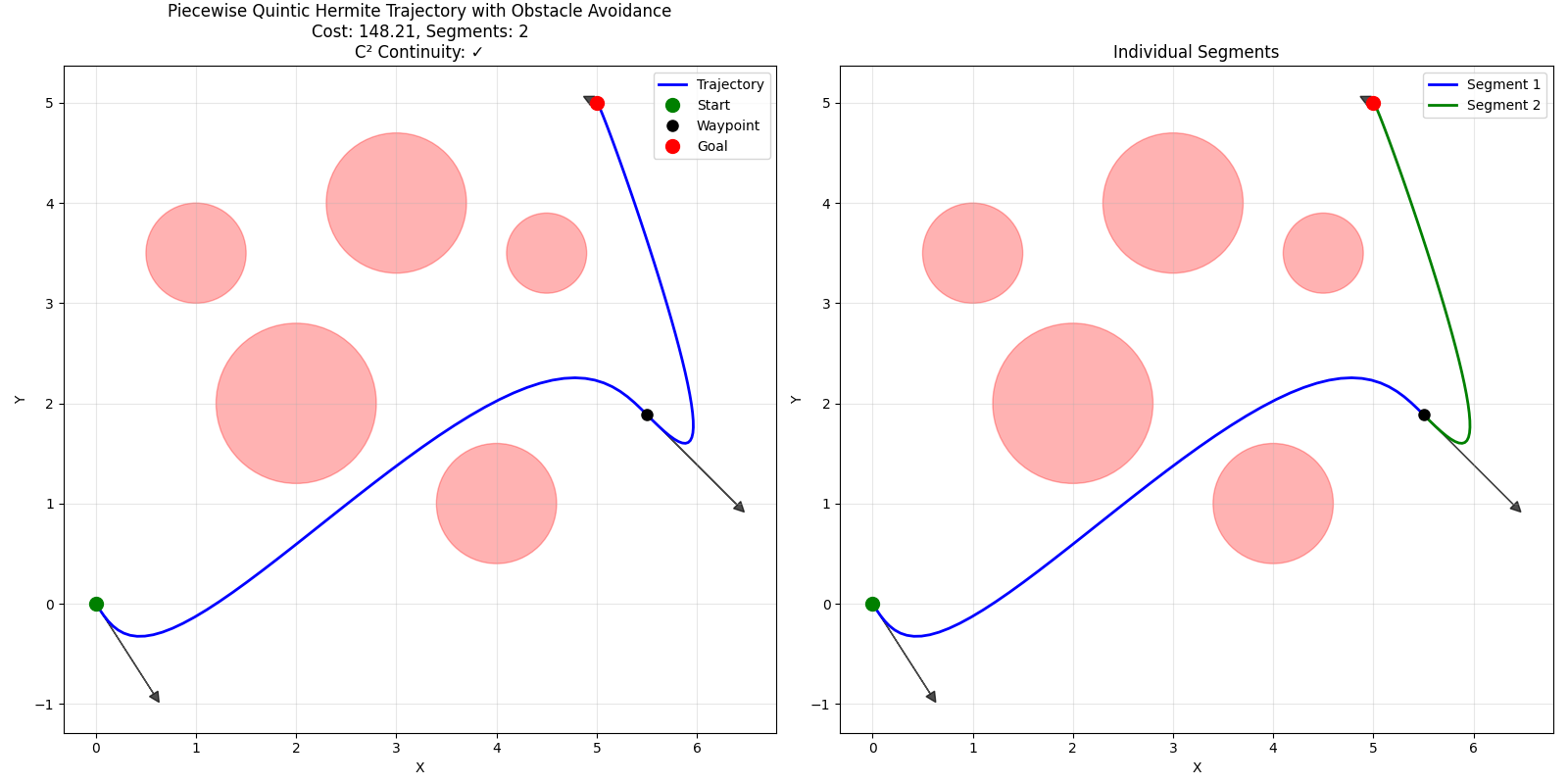
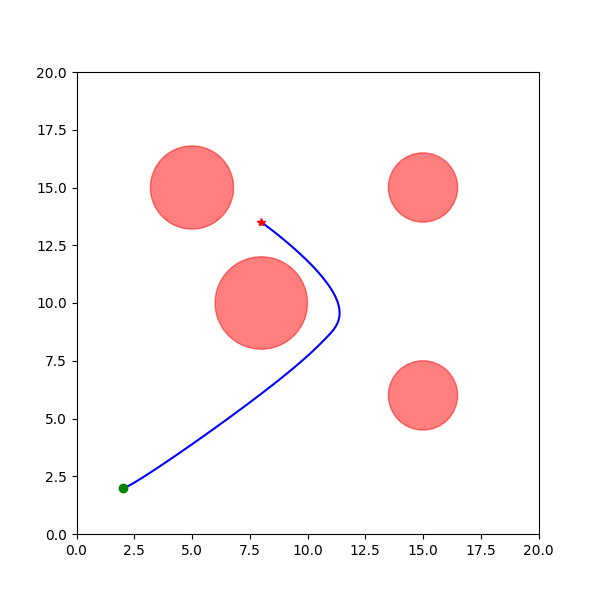
Experiments